The Primary Causes And Treatment Plans For Achilles Tendonitis Aches
Overview
 The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
Causes
There are hundreds of tendons scattered throughout our body, but it tends to be a small handful of specific tendons that cause problems. These tendons usually have an area of poor blood supply that leads to tissue damage and poor healing response. This area of a tendon that is prone to injury is called a "watershed zone," an area when the blood supply to the tendon is weakest. In these watershed zones, they body has a hard time delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for tendon healing, that's why we see common tendon problems in the same parts of the body. Tendonitis is most often an overuse injury. Often people begin a new activity or exercise that causes the tendon to become irritated. Tendon problems are most common in the 40-60 year old age range. Tendons are not as elastic and forgiving as in younger individuals, yet bodies are still exerting with the same force. Occasionally, there is an anatomical cause for tendonitis. If the tendon does not have a smooth path to glide along, it will be more likely to become irritated and inflamed. In these unusual situations, surgical treatment may be necessary to realign the tendon.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of Achilles tendon inflammation is pain in the back of the heel, which initially increases when exercise is begun and often lessens as exercise continues. A complete tear of the Achilles tendon typically occurs with a sudden forceful change in direction when running or playing tennis and is often accompanied by a sensation of having been struck in the back of the ankle and calf with an object such as a baseball bat.
Diagnosis
If you think you have Achilles tendinitis, make an appointment to see your doctor. The doctor will ask you questions about your recent activity and look for signs. The foot not flexing when the calf muscle is pressed ( if Achilles ruptures or tears in half). Swelling on the back of the foot. Pain in the back of the foot. Limited range of motion in ankle. An X-ray or MRI scan can check for tendinitis.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment for achilles tendonitis is based around initially reducing pain and inflammation, stretching the muscles out and a gradual return to activity. No one single approach may cure achilles tendonitis, particularly a chronic condition but a combination of treatment approaches and patience will work best. It is essential the correct treatment is started as soon as possible in the acute stage to avoid the injury becoming chronic. Acute achilles tendonitis requires rest. Continuing to train on a painful achilles tendon could lead to the injury becoming chronic and more difficult to treat. Applying ice or cold therapy as soon as possible to a painful achilles tendon will reduce pain and inflammation. After the first 24 to 48 hours alternating hot and cold or just heat may be more beneficial. Tendons work better when they are warm but if they are painful then rest and ice. Wear a heel pad to raise the heel and shorten the calf muscles which in turn reduces some of the strain on the achilles tendon. This should only be a temporary measure while the achilles tendon is healing. An achilles tendon taping technique can aid rest by supporting the tendon with elastic bandages. This is an excellent way of taking the load off the tendon if you have to walk around on your feet as well as protecting the tendon when returning to full fitness. Achilles tendon exercisesMake sure you have the right running shoes for your foot type and the sport. If you are a runner that over-pronates then a motion control or support running shoe may be needed. Visit a specialist running shop for advice. In the later stages apply heat, especially before exercise. The tendon will perform better when warm. Finish with cold after training to reduce any inflammation.
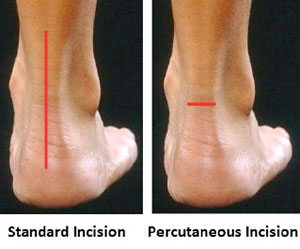
Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical treatment fails to cure the condition then surgery can be considered. This is more likely to be the case if the pain has been present for six months or more. The nature of the surgery depends if you have insertional, or non-insertional disease. In non-insertional tendonosis the damaged tendon is thinned and cleaned. The damage is then repaired. If there is extensive damage one of the tendons which moves your big toe (the flexor hallucis longus) may be used to reinforce the damaged Achilles tendon. In insertional tendonosis there is often rubbing of the tendon by a prominent part of the heel bone. This bone is removed. In removing the bone the attachment of the tendon to the bone may be weakened. In these cases the attachment of the tendon to the bone may need to be reinforced with sutures and bone anchors.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or non-surgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.
 The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
Causes
There are hundreds of tendons scattered throughout our body, but it tends to be a small handful of specific tendons that cause problems. These tendons usually have an area of poor blood supply that leads to tissue damage and poor healing response. This area of a tendon that is prone to injury is called a "watershed zone," an area when the blood supply to the tendon is weakest. In these watershed zones, they body has a hard time delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for tendon healing, that's why we see common tendon problems in the same parts of the body. Tendonitis is most often an overuse injury. Often people begin a new activity or exercise that causes the tendon to become irritated. Tendon problems are most common in the 40-60 year old age range. Tendons are not as elastic and forgiving as in younger individuals, yet bodies are still exerting with the same force. Occasionally, there is an anatomical cause for tendonitis. If the tendon does not have a smooth path to glide along, it will be more likely to become irritated and inflamed. In these unusual situations, surgical treatment may be necessary to realign the tendon.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of Achilles tendon inflammation is pain in the back of the heel, which initially increases when exercise is begun and often lessens as exercise continues. A complete tear of the Achilles tendon typically occurs with a sudden forceful change in direction when running or playing tennis and is often accompanied by a sensation of having been struck in the back of the ankle and calf with an object such as a baseball bat.
Diagnosis
If you think you have Achilles tendinitis, make an appointment to see your doctor. The doctor will ask you questions about your recent activity and look for signs. The foot not flexing when the calf muscle is pressed ( if Achilles ruptures or tears in half). Swelling on the back of the foot. Pain in the back of the foot. Limited range of motion in ankle. An X-ray or MRI scan can check for tendinitis.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment for achilles tendonitis is based around initially reducing pain and inflammation, stretching the muscles out and a gradual return to activity. No one single approach may cure achilles tendonitis, particularly a chronic condition but a combination of treatment approaches and patience will work best. It is essential the correct treatment is started as soon as possible in the acute stage to avoid the injury becoming chronic. Acute achilles tendonitis requires rest. Continuing to train on a painful achilles tendon could lead to the injury becoming chronic and more difficult to treat. Applying ice or cold therapy as soon as possible to a painful achilles tendon will reduce pain and inflammation. After the first 24 to 48 hours alternating hot and cold or just heat may be more beneficial. Tendons work better when they are warm but if they are painful then rest and ice. Wear a heel pad to raise the heel and shorten the calf muscles which in turn reduces some of the strain on the achilles tendon. This should only be a temporary measure while the achilles tendon is healing. An achilles tendon taping technique can aid rest by supporting the tendon with elastic bandages. This is an excellent way of taking the load off the tendon if you have to walk around on your feet as well as protecting the tendon when returning to full fitness. Achilles tendon exercisesMake sure you have the right running shoes for your foot type and the sport. If you are a runner that over-pronates then a motion control or support running shoe may be needed. Visit a specialist running shop for advice. In the later stages apply heat, especially before exercise. The tendon will perform better when warm. Finish with cold after training to reduce any inflammation.

Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical treatment fails to cure the condition then surgery can be considered. This is more likely to be the case if the pain has been present for six months or more. The nature of the surgery depends if you have insertional, or non-insertional disease. In non-insertional tendonosis the damaged tendon is thinned and cleaned. The damage is then repaired. If there is extensive damage one of the tendons which moves your big toe (the flexor hallucis longus) may be used to reinforce the damaged Achilles tendon. In insertional tendonosis there is often rubbing of the tendon by a prominent part of the heel bone. This bone is removed. In removing the bone the attachment of the tendon to the bone may be weakened. In these cases the attachment of the tendon to the bone may need to be reinforced with sutures and bone anchors.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or non-surgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.
What Exactly Triggers Pain At The Heel

Overview
Heel pain is a common foot condition. It's usually felt as an intense pain when using the affected heel. Heel pain usually builds up gradually and gets worse over time. The pain is often severe and occurs when you place weight on the heel. In most cases, only one heel is affected, although estimates suggest that around a third of people have pain in both heels. The pain is usually worse first thing in the morning, or when you first take a step after a period of inactivity. Walking usually improves the pain, but it often gets worse again after walking or standing for a long time. Some people may limp or develop an abnormal walking style as they try to avoid placing weight on the affected heel.
Causes
Although plantar fasciitis may result from a variety of factors, such as repeat hill workouts and/or tight calves, many sports specialists claim the most common cause for plantar fasciitis is fallen arches. The theory is that excessive lowering of the arch in flat-footed runners increases tension in the plantar fascia and overloads the attachment of the plantar fascia on the heel bone (i.e., the calcaneus). Over time, the repeated pulling of the plantar fascia associated with excessive arch lowering is thought to lead to chronic pain and inflammation at the plantar fascia’s attachment to the heel. In fact, the increased tension on the heel was believed to be so great that it was thought to eventually result in the formation of a heel spur.
Symptoms
Pain is the main symptom. This can be anywhere on the underside of your heel. However, commonly, one spot is found as the main source of pain. This is often about 4 cm forward from your heel, and may be tender to touch. The pain is often worst when you take your first steps on getting up in the morning, or after long periods of rest where no weight is placed on your foot. Gentle exercise may ease things a little as the day goes by, but a long walk or being on your feet for a long time often makes the pain worse. Resting your foot usually eases the pain. Sudden stretching of the sole of your foot may make the pain worse, for example, walking up stairs or on tiptoes. You may limp because of pain. Some people have plantar fasciitis in both feet at the same time.
Diagnosis
Your doctor may look at your feet and watch the way you stand, walk and exercise. He can also ask you questions about your health history, including illnesses and injuries that you had in your past. The symptoms you have such as the pain location or when does your foot hurts most. Your activity routine such as your job, exercise habits and physical activities preformed. Your doctor may decide to use an X-ray of your foot to detect bones problems. MRI or ultrasound can also be used as further investigation of the foot condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
A steroid (cortisone) injection is sometimes tried if your pain remains bad despite the above 'conservative' measures. It may relieve the pain in some people for several weeks but does not always cure the problem. It is not always successful and may be sore to have done. Steroids work by reducing inflammation. Sometimes two or three injections are tried over a period of weeks if the first is not successful. Steroid injections do carry some risks, including (rarely) tearing (rupture) of the plantar fascia. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy. In extracorporeal shock-wave therapy, a machine is used to deliver high-energy sound waves through your skin to the painful area on your foot. It is not known exactly how it works, but it is thought that it might stimulate healing of your plantar fascia. One or more sessions of treatment may be needed. This procedure appears to be safe but it is uncertain how well it works. This is mostly because of a lack of large, well-designed clinical trials. You should have a full discussion with your doctor about the potential benefits and risks. In studies, most people who have had extracorporeal shock-wave therapy have little in the way of problems. However, possible problems that can occur include pain during treatment, skin reddening, and swelling of your foot or bruising. Another theoretical problem could include the condition getting worse because of rupture of your plantar fascia or damage to the tissues in your foot. More research into extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for plantar fasciitis is needed. Other treatments. Various studies and trials have been carried out looking at other possible treatments for plantar fasciitis. Such treatments include injection with botulinum toxin and treatment of the plantar fascia with radiotherapy. These treatments may not be widely available. Some people benefit from wearing a special splint overnight to keep their Achilles tendon and plantar fascia slightly stretched. The aim is to prevent the plantar fascia from tightening up overnight. In very difficult cases, sometimes a plaster cast or a removable walking brace is put on the lower leg. This provides rest, protection, cushioning and slight stretching of the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon. However, the evidence for the use of splint treatment of plantar fasciitis is limited.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery for plantar fasciitis can be very successful in the right patients. While there are potential complications, about 70-80% of patients will find relief after plantar fascia release surgery. This may not be perfect, but if plantar fasciitis has been slowing you down for a year or more, it may well be worth these potential risks of surgery. New surgical techniques allow surgery to release the plantar fascia to be performed through small incisions using a tiny camera to locate and cut the plantar fascia. This procedure is called an endoscopic plantar fascia release. Some surgeons are concerned that the endoscopic plantar fascia release procedure increases the risk of damage to the small nerves of the foot. While there is no definitive answer that this endoscopic plantar fascia release is better or worse than a traditional plantar fascia release, most surgeons still prefer the traditional approach.
Prevention
Factors that help prevent plantar fasciitis and reduce the risk of recurrence include. Exercises to strengthen the muscles of the lower leg and ankle. Warming up before commencing physical activity. Maintaining a healthy body weight. Avoiding high heeled footwear. Using orthotic devices such as arch supports and heel raises in footwear, particularly for people with very high arches or flat feet. Daily stretches of plantar fascia and Achilles tendon.
What Is Pain In The Heel And The Right Way To Fix It

Overview
Plantar Fasciitis is a common athletic injury of the foot. While runners are most likely to suffer from plantar fasciitis, any athlete whose sport involves intensive use of the feet may be vulnerable. The risk of plantar fasciitis increases in athletes who have a particularly high arch, or uneven leg length, though improper biomechanics of the athlete’s gait and simple overuse tend to be the primary culprits. If you suffer from plantar fasciitis or are seeking to prevent its occurrence it is important to follow the information in this article. In addition, adding a few simple stretches to your fitness program will also help.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is caused by drastic or sudden increases in mileage, poor foot structure, and inappropriate running shoes, which can overload the plantar fascia, the connective tissue that runs from the heel to the base of the toes. The plantar fascia may look like a series of fat rubber bands, but it's made of collagen, a rigid protein that's not very stretchy. The stress of overuse, overpronation, or overused shoes can rip tiny tears in it, causing pain and inflammation, a.k.a. plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciosis is characterized by pain at the bottom of the heel with weight bearing, particularly when first arising in the morning; pain usually abates within 5 to 10 min, only to return later in the day. It is often worse when pushing off of the heel (the propulsive phase of gait) and after periods of rest. Acute, severe heel pain, especially with mild local puffiness, may indicate an acute fascial tear. Some patients describe burning or sticking pain along the plantar medial border of the foot when walking.
Diagnosis
A physical exam performed in the office along with the diagnostic studies as an x-ray. An MRI may also be required to rule out a stress fracture, or a tear of the plantar fascia. These are conditions that do not normally respond to common plantar fasciitis treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
Careful attention to footwear is critical. Every effort should be made to wear comfortable shoes with proper arch support, fostering proper foot posture. Should arch supports prove insufficient, an orthotic shoe should be considered. Fortunately, most cases of plantar fasciitis respond well to non-operative treatment. Recovery times however vary enormously from one athlete to another, depending on age, overall health and physical condition as well as severity of injury. A broad period between 6 weeks and 6 months is usually sufficient for proper healing. Additionally, the mode of treatment must be flexible depending on the details of a particular athlete’s injury. Methods that prove successful in one patient, may not improve the injury in another. Early treatment typically includes the use of anti-inflammatory medication, icing, stretching activities, and heel inserts and splints. Cortisone injections may be necessary to achieve satisfactory healing and retard inflammation. In later stages of the rehabilitation process, typically after the first week, ice should be discontinued and replaced with heat and massage.

Surgical Treatment
In unusual cases, surgical intervention is necessary for relief of pain. These should only be employed after non-surgical efforts have been used without relief. Generally, such surgical procedures may be completed on an outpatient basis in less than one hour, using local anesthesia or minimal sedation administrated by a trained anesthesiologist. In such cases, the surgeon may remove or release the injured and inflamed fascia, after a small incision is made in the heel. A surgical procedure may also be undertaken to remove bone spurs, sometimes as part of the same surgery addressing the damaged tissue. A cast may be used to immobilize the foot following surgery and crutches provided in order to allow greater mobility while keeping weight off the recovering foot during healing. After removal of the cast, several weeks of physical therapy can be used to speed recovery, reduce swelling and restore flexibility.
Prevention
You can help to prevent plantar fasciitis by maintaining a healthy weight, by warming up before participating in sports and by wearing shoes that support the arch and cushion the heel. In people who are prone to episodes of plantar fasciitis, exercises that stretch the heel cord (known as the Achilles tendon) and the plantar fascia may help to prevent plantar fasciitis from returning. Ice massage also can be used on the bottom of the foot after stressful athletic activities. It is possible that strict control of blood sugar will prevent plantar fasciitis in people with diabetes, although this has not been proven.
What Is Heel Pain
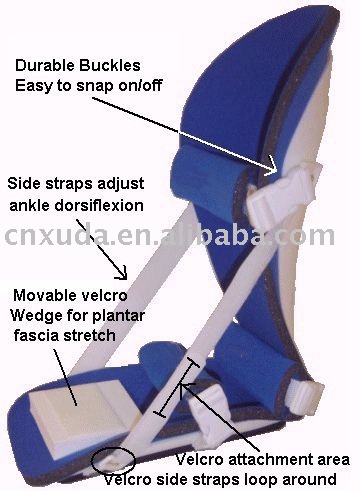
Overview
Plantar fasciitis often occurs in middle-age. It also occurs in people who spend long hours standing on their feet at work, like athletes or soldiers. It can happen in one foot or both feet. It is common in sports like long distance running, dancing etc. Athletes who overpronate (rolling in or flattening feet) are especially at risk as the biomechanics of their feet place more stress to the band. Plantar fasciitis can take a long time to heal. Six months is the average time reported in medical research. There are some who will get cured after a few weeks and for others it will take more than a year. It can also become a chronic condition in which case some sort of treatment will always be needed to prevent the pain from coming back. As sooner as the condition is treated chances are it will not get chronic or in other words if you treat plantar fasciitis sooner you will get cured faster.
Causes
Patients with tight calf muscles will suffer with excessive pulling of the muscle group on the back of the heel. This in turn creates pulling of other structures that are attached to the heel, including the Plantar Fascia. When the pulling continues for long enough, then inflammation will develop and lead to Plantar Fasciitis. This causes Heel Pain. It is extremely common for patients who increase their level of activity to develop Plantar Fasciitis. Boot camp, running, zumba, recreational walking or other quick movement sports such as tennis or touch football are typical causes of Heel Pain. The sharp increase in exercise is too much for the foot to cope with and the stress on the Plantar Fascia causes inflammation. The Heel Pain that is caused by this inflammation is known as Plantar Fasciitis.
Symptoms
Heel pain is the most common symptom associated with plantar fasciosis. Your heel pain may be worse in the morning or after you have been sitting or standing for long periods. Pain is most common under your heel bone, but you also may experience pain in your foot arch or on the outside aspect of your foot. Other common signs and symptoms of plantar fasciosis include mild swelling and redness in your affected area, tenderness on the bottom of your heel, impaired ability to ambulate.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
Many cases of plantar fasciitis can be treated with simple, conservative measures. These include ice packs, stretching exercises, anti-inflammatory medications, orthotic devices (custom molded orthotics), and physical therapy. It’s important to consult your doctor before you take any medications to treat this condition. In chronic or persistent cases, one of three techniques may be used to treat plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment (ESWT). TOPAZ treatment. Platelet Rich P
lasma therapy.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely used in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. However it may be recommended when conservative treatment has been tried for several months but does not bring adequate relief of symptoms. Surgery usually involves the partial release of the plantar fascia from the heel bone. In approximately 75% of cases symptoms are fully resolved within six months. In a small percentage of cases, symptoms may take up to 12 months to fully resolve.
Stretching Exercises
Exercises designed to stretch both your calf muscles and your plantar fascia (the band of tissue that runs under the sole of your foot) should help relieve pain and improve flexibility in the affected foot. A number of stretching exercises are described below. It's usually recommended that you do the exercises on both legs, even if only one of your heels is affected by pain. This will improve your balance and stability, and help relieve heel pain. Towel stretches. Keep a long towel beside your bed. Before you get out of bed in the morning, loop the towel around your foot and use it to pull your toes towards your body, while keeping your knee straight. Repeat three times on each foot. Wall stretches. Place both hands on a wall at shoulder height, with one of your feet in front of the other. The front foot should be about 30cm (12 inches) away from the wall. With your front knee bent and your back leg straight, lean towards the wall until you feel a tightening in the calf muscles of your back leg. Then relax. Repeat this exercise 10 times before switching legs and repeating the cycle. You should practise wall stretches twice a day. Stair stretches. Stand on a step of your stairs facing upstairs, using your banister for support. Your feet should be slightly apart, with your heels hanging off the back of the step. Lower your heels until you feel a tightening in your calves. Hold this position for about 40 seconds, before raising your heels back to the starting position. Repeat this procedure six times, at least twice a day. Chair stretches. Sit on a chair, with your knees bent at right angles. Turn your feet sideways so your heels are touching and your toes are pointing in opposite directions. Lift the toes of the affected foot upwards, while keeping the heel firmly on the floor. You should feel your calf muscles and Achilles tendon (the band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your calf muscle) tighten. Hold this position for several seconds and then relax. Repeat this procedure 10 times, five to six times a day. Dynamic stretches. While seated, roll the arch of your foot (the curved bottom part of the foot between your toes and heel) over a round object, such as a rolling pin, tennis ball or drinks can. Some people find that using a chilled can from their fridge has the added benefit of helping to relieve pain. Move your foot and ankle in all directions over the object for several minutes. Repeat the exercise twice a day.
Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Foot and Ankle
Metatarsal pain, often referred to as metatarsalgia, can be caused by several foot conditions, including Freiberg's disease, Morton's neuroma and sesamoiditis. According to a 2003 article in the British Journal of Sports Bunions Hard Skin Medicine,” a flat or high arch is one of many risk factors for lower extremity injuries including foot injuries. Poor circulation occurs when there is not enough blood supplied to an area to meet the needs of the cells.
Orthotics are shoe insoles, custom-made to guide the foot into corrected biomechanics. Orthotics are commonly prescribed to help with hammer toes, heel spurs, metatarsal problems, bunions, diabetic ulcerations and numerous other problems. They also help to minimize shin splints, back pain and strain on joints and ligaments. Orthotics help foot problems by ensuring proper foot mechanics and taking pressure off the parts of your foot that you are placing too much stress on. Dr. Cherine's mission is to help you realize your greatest potential and live your life to its fullest.
Pain often occurs suddenly and mainly around the undersurface of the heel, although it often spreads to your arch. The condition can be temporary, but may become chronic if you ignore it. Resting usually provides relief, but the pain may return. Heel spurs are bony growths that protrude from the bottom of the heel bone, and they are parallel to the ground. There is a nerve that runs very close to this area and may contribute to the pain which occurs.
Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.
During the average lifetime our feet cover over 70,000 miles, the equivalent of walking four times around the world., so it's not surprising that problems can occur. Indeed around three-quarters of all adults will experience some sort of problem with their feet at some time. And without treatment most foot complaints will become gradually worse with time. This means people often endure painful conditions for far too long, and the problem can get worse. People often assume nothing can be done to help their condition, but in fact these conditions are extremely treatable. Swollen lump on big toe joint; lump may become numb but also make walking painful.
Orthotics are shoe insoles, custom-made to guide the foot into corrected biomechanics. Orthotics are commonly prescribed to help with hammer toes, heel spurs, metatarsal problems, bunions, diabetic ulcerations and numerous other problems. They also help to minimize shin splints, back pain and strain on joints and ligaments. Orthotics help foot problems by ensuring proper foot mechanics and taking pressure off the parts of your foot that you are placing too much stress on. Dr. Cherine's mission is to help you realize your greatest potential and live your life to its fullest.
Pain often occurs suddenly and mainly around the undersurface of the heel, although it often spreads to your arch. The condition can be temporary, but may become chronic if you ignore it. Resting usually provides relief, but the pain may return. Heel spurs are bony growths that protrude from the bottom of the heel bone, and they are parallel to the ground. There is a nerve that runs very close to this area and may contribute to the pain which occurs.

Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.

During the average lifetime our feet cover over 70,000 miles, the equivalent of walking four times around the world., so it's not surprising that problems can occur. Indeed around three-quarters of all adults will experience some sort of problem with their feet at some time. And without treatment most foot complaints will become gradually worse with time. This means people often endure painful conditions for far too long, and the problem can get worse. People often assume nothing can be done to help their condition, but in fact these conditions are extremely treatable. Swollen lump on big toe joint; lump may become numb but also make walking painful.
Achilles Tendinitis
Overview
 The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It is formed by the merging together of the upper calf muscles and inserts into the back of the heel bone. Its blood supply comes from the muscles above and the bony attachment below. The blood supply is limited at the ?watershed? zone approximately 1 to 4 inches above the insertion into the heel bone. Paratendonitis and tendinosis develop in the same area. Achilles tendinitis implies an inflammatory response, but this is very limited because there is little blood supply to the Achilles tendon. More appropriate descriptions are inflammation of the surrounding sheath (paratenonitis), degeneration within the substance of the tendon (tendinosis) or a combination of the two.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It is formed by the merging together of the upper calf muscles and inserts into the back of the heel bone. Its blood supply comes from the muscles above and the bony attachment below. The blood supply is limited at the ?watershed? zone approximately 1 to 4 inches above the insertion into the heel bone. Paratendonitis and tendinosis develop in the same area. Achilles tendinitis implies an inflammatory response, but this is very limited because there is little blood supply to the Achilles tendon. More appropriate descriptions are inflammation of the surrounding sheath (paratenonitis), degeneration within the substance of the tendon (tendinosis) or a combination of the two.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis is caused by repetitive or intense strain on the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. This tendon is used when you walk, run, jump or push up on your toes. The structure of the Achilles tendon weakens with age, which can make it more susceptible to injury - particularly in people who may participate in sports only on the weekends or who have suddenly increased the intensity of their running programs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of acute achilles tendonitis will be a gradual onset of achilles pain at the back of the ankle, just above the heel bone. This may develop over a period of days. The achilles tendon may be painful and stiff at the start of exercise and first thing in the morning. As the tendon warms up the pain will go often for it to return later in the day or towards the end of a prolonged training session. The tendon will be very tender on palpation or pressing in on the achilles tendon or squeezing it from the sides. Chronic achilles tendonitis may follow on from acute achilles tendonitis if it goes untreated or is not allowed sufficient rest. Chronic achilles tendonitis is a difficult condition to treat, particularly in older athletes who appear to suffer more often.
Diagnosis
Physicians usually pinch your Achilles tendon with their fingers to test for swelling and pain. If the tendon itself is inflamed, your physician may be able to feel warmth and swelling around the tissue, or, in chronic cases, lumps of scar tissue. You will probably be asked to walk around the exam room so your physician can examine your stride. To check for complete rupture of the tendon, your physician may perform the Thompson test. Your physician squeezes your calf; if your Achilles is not torn, the foot will point downward. If your Achilles is torn, the foot will remain in the same position. Should your physician require a closer look, these imaging tests may be performed. X-rays taken from different angles may be used to rule out other problems, such as ankle fractures. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic waves to create pictures of your ankle that let physicians more clearly look at the tendons surrounding your ankle joint.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment will depend on the severity of the injury. In general terms, the longer the symptoms are present before treatment begins, the longer the timeframe until complete recovery is achieved. Complete recovery can take between three and nine months. Initial treatment of Achilles tendonitis includes, Rest, to avoid further injury to the area. Ice, to reduce inflammation, Elevation, to reduce swelling. Bandaging or strapping, to support the area and restrict movement of the tendon. Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation. (Cortisone (steroid) injections to reduce inflammation are not usually recommended as they may weaken the tendon and increase the risk of rupture). Other treatments include, Physiotherapy, Physiotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of Achilles tendonitis. This generally focuses on two main areas - treatment and rehabilitation. Treatment may involve such techniques as massage, ultrasound, acupuncture and gentle stretching. Rehabilitation involves the development of an individualised recovery programme, the most important aspect of which is strengthening. Strengthening of the muscles surrounding the Achilles tendon helps to promote healing in the tendon itself. Strengthening is achieved through the use of specific exercises, which will be taught by the physiotherapist. One such exercise is eccentric loading, which involves contracting the calf muscle while it is being stretched. It is common for the rehabilitation programme to take up to three months. Podiatry, including gait analysis and the fitting of orthotic devices to support the foot and reduce stress on the tendon, may be recommended. For cases of Achilles tendonitis that do not respond to initial treatment, casting or splinting of the affected foot may be recommended to allow it to rest completely.

Surgical Treatment
As with any surgery there are risks to every procedure depending on a lot of factors, including your age, the severity of your injury and your level of health going into the procedure. It is always best to discuss all possible risks and complications with your doctor, orthopaedic specialist and/or surgeon before the procedure. It's important to be aware of the risks you may face with any procedure intended to fix or relieve pain from your Achilles tendon injury.
Prevention
Do strengthening and stretching exercises to keep calf muscles strong and flexible. Keep your hamstring muscles flexible by stretching. Warm up and stretch adequately before participating in any sports. Always increase the intensity and duration of training gradually. Do not continue an exercise if you experience pain over the tendon. Wear properly fitted running and other sports shoes, including properly fitted arch supports if your feet roll inwards excessively (over-pronate).
 The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It is formed by the merging together of the upper calf muscles and inserts into the back of the heel bone. Its blood supply comes from the muscles above and the bony attachment below. The blood supply is limited at the ?watershed? zone approximately 1 to 4 inches above the insertion into the heel bone. Paratendonitis and tendinosis develop in the same area. Achilles tendinitis implies an inflammatory response, but this is very limited because there is little blood supply to the Achilles tendon. More appropriate descriptions are inflammation of the surrounding sheath (paratenonitis), degeneration within the substance of the tendon (tendinosis) or a combination of the two.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It is formed by the merging together of the upper calf muscles and inserts into the back of the heel bone. Its blood supply comes from the muscles above and the bony attachment below. The blood supply is limited at the ?watershed? zone approximately 1 to 4 inches above the insertion into the heel bone. Paratendonitis and tendinosis develop in the same area. Achilles tendinitis implies an inflammatory response, but this is very limited because there is little blood supply to the Achilles tendon. More appropriate descriptions are inflammation of the surrounding sheath (paratenonitis), degeneration within the substance of the tendon (tendinosis) or a combination of the two.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis is caused by repetitive or intense strain on the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. This tendon is used when you walk, run, jump or push up on your toes. The structure of the Achilles tendon weakens with age, which can make it more susceptible to injury - particularly in people who may participate in sports only on the weekends or who have suddenly increased the intensity of their running programs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of acute achilles tendonitis will be a gradual onset of achilles pain at the back of the ankle, just above the heel bone. This may develop over a period of days. The achilles tendon may be painful and stiff at the start of exercise and first thing in the morning. As the tendon warms up the pain will go often for it to return later in the day or towards the end of a prolonged training session. The tendon will be very tender on palpation or pressing in on the achilles tendon or squeezing it from the sides. Chronic achilles tendonitis may follow on from acute achilles tendonitis if it goes untreated or is not allowed sufficient rest. Chronic achilles tendonitis is a difficult condition to treat, particularly in older athletes who appear to suffer more often.
Diagnosis
Physicians usually pinch your Achilles tendon with their fingers to test for swelling and pain. If the tendon itself is inflamed, your physician may be able to feel warmth and swelling around the tissue, or, in chronic cases, lumps of scar tissue. You will probably be asked to walk around the exam room so your physician can examine your stride. To check for complete rupture of the tendon, your physician may perform the Thompson test. Your physician squeezes your calf; if your Achilles is not torn, the foot will point downward. If your Achilles is torn, the foot will remain in the same position. Should your physician require a closer look, these imaging tests may be performed. X-rays taken from different angles may be used to rule out other problems, such as ankle fractures. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic waves to create pictures of your ankle that let physicians more clearly look at the tendons surrounding your ankle joint.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment will depend on the severity of the injury. In general terms, the longer the symptoms are present before treatment begins, the longer the timeframe until complete recovery is achieved. Complete recovery can take between three and nine months. Initial treatment of Achilles tendonitis includes, Rest, to avoid further injury to the area. Ice, to reduce inflammation, Elevation, to reduce swelling. Bandaging or strapping, to support the area and restrict movement of the tendon. Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation. (Cortisone (steroid) injections to reduce inflammation are not usually recommended as they may weaken the tendon and increase the risk of rupture). Other treatments include, Physiotherapy, Physiotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of Achilles tendonitis. This generally focuses on two main areas - treatment and rehabilitation. Treatment may involve such techniques as massage, ultrasound, acupuncture and gentle stretching. Rehabilitation involves the development of an individualised recovery programme, the most important aspect of which is strengthening. Strengthening of the muscles surrounding the Achilles tendon helps to promote healing in the tendon itself. Strengthening is achieved through the use of specific exercises, which will be taught by the physiotherapist. One such exercise is eccentric loading, which involves contracting the calf muscle while it is being stretched. It is common for the rehabilitation programme to take up to three months. Podiatry, including gait analysis and the fitting of orthotic devices to support the foot and reduce stress on the tendon, may be recommended. For cases of Achilles tendonitis that do not respond to initial treatment, casting or splinting of the affected foot may be recommended to allow it to rest completely.

Surgical Treatment
As with any surgery there are risks to every procedure depending on a lot of factors, including your age, the severity of your injury and your level of health going into the procedure. It is always best to discuss all possible risks and complications with your doctor, orthopaedic specialist and/or surgeon before the procedure. It's important to be aware of the risks you may face with any procedure intended to fix or relieve pain from your Achilles tendon injury.
Prevention
Do strengthening and stretching exercises to keep calf muscles strong and flexible. Keep your hamstring muscles flexible by stretching. Warm up and stretch adequately before participating in any sports. Always increase the intensity and duration of training gradually. Do not continue an exercise if you experience pain over the tendon. Wear properly fitted running and other sports shoes, including properly fitted arch supports if your feet roll inwards excessively (over-pronate).
All The Things You Want To Know Concerning Achilles Tendinitis
Overview
 Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis can be caused by any activity that puts stress on your Achilles tendon. Tendinitis can develop if you run or jump more than usual or exercise on a hard surface. Tendinitis can be caused by shoes that do not fit or support your foot and ankle. Tight tendons and muscles, You may have tight hamstring and calf muscles in your upper and lower leg. Your tendons also become stiffer and easier to injure as you get older. Arthritis, Bony growths caused by arthritis can irritate the Achilles tendon, especially around your heel.
Symptoms
Achilles tendonitis is an injury that occurs when your Achilles tendon -- the large band of tissues connecting the muscles in the back of your lower leg to your heel bone -- becomes inflamed or irritated. The signs and symptoms of Achilles tendonitis often develop gradually. You'll feel pain and stiffness in your Achilles, especially when you first get out of bed. The pain lessens as you warm up, and may even disappear as you continue running. Once you stop, the pain returns and may feel even worse. You may also notice a crackling or creaking sound when you touch or move your Achilles tendon.
Diagnosis
In diagnosing Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis, the surgeon will examine the patient?s foot and ankle and evaluate the range of motion and condition of the tendon. The extent of the condition can be further assessed with x-rays or other imaging modalities.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The best treatment for Achilles tendonitis is preventative, stretching and warming up properly before starting an activity. Proper rest, accompanied by stretching and icing to reduce swelling, can help to heal an overworked Achilles tendon. Placing an adequate heel lift in both shoes will allow the heel to have contact with the ground without placing stress on the Achilles tendon. Wear a tie shoe that is stiff soled and has a wide base, then add an over-the-counter or custom foot orthosis inside the shoe to prevent the twisting motion of the Achilles tendon due to over pronation. In the event that the tendon is unable to heal due to your life style or activity, you may have to be put in a walking cast for a short period to give it a chance to heal. You need to have the doctor, physical therapist, or come in to our facility to check for a leg length difference due to the walking cast being higher. This is to prevent any discomfort to the hips. After the tendon has healed and before the foot is taken out of the walking cast, range of motion at the ankle must be tested and if the foot is not allowed to properly bend upwards 15 degrees then the tightness in the calf will cause the foot to over pronate and reinjure. A stretching program will be needed to loosen up the calf muscle before much weight bearing is done without the cast. The stretching program can be found at the menu for feet hurt. If necessary a heel lift can be put in both shoes to help take the stress off the tendon. Should the tightness of the calves be the primary cause for the Achilles tendon damage and stretching has not loosen the Achilles tendon sufficiently, then discussion with your doctor for a calf release may have to be considered.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered the last resort and is often performed by an orthopedic surgeon. It is only recommended if all other treatment options have failed after at least six months. In this situation, badly damaged portions of the tendon may be removed. If the tendon has ruptured, surgery is necessary to re-attach the tendon. Rehabilitation, including stretching and strength exercises, is started soon after the surgery. In most cases, normal activities can be resumed after about 10 weeks. Return to competitive sport for some people may be delayed for about three to six months.
Prevention
If you're just getting started with your training, be sure to stretch after running, and start slowly, increasing your mileage by no more than 10% per week. Strengthen your calf muscles with exercises such as toe raises. Work low-impact cross-training activities, such as cycling and swimming, into your training.
 Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis can be caused by any activity that puts stress on your Achilles tendon. Tendinitis can develop if you run or jump more than usual or exercise on a hard surface. Tendinitis can be caused by shoes that do not fit or support your foot and ankle. Tight tendons and muscles, You may have tight hamstring and calf muscles in your upper and lower leg. Your tendons also become stiffer and easier to injure as you get older. Arthritis, Bony growths caused by arthritis can irritate the Achilles tendon, especially around your heel.
Symptoms
Achilles tendonitis is an injury that occurs when your Achilles tendon -- the large band of tissues connecting the muscles in the back of your lower leg to your heel bone -- becomes inflamed or irritated. The signs and symptoms of Achilles tendonitis often develop gradually. You'll feel pain and stiffness in your Achilles, especially when you first get out of bed. The pain lessens as you warm up, and may even disappear as you continue running. Once you stop, the pain returns and may feel even worse. You may also notice a crackling or creaking sound when you touch or move your Achilles tendon.
Diagnosis
In diagnosing Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis, the surgeon will examine the patient?s foot and ankle and evaluate the range of motion and condition of the tendon. The extent of the condition can be further assessed with x-rays or other imaging modalities.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The best treatment for Achilles tendonitis is preventative, stretching and warming up properly before starting an activity. Proper rest, accompanied by stretching and icing to reduce swelling, can help to heal an overworked Achilles tendon. Placing an adequate heel lift in both shoes will allow the heel to have contact with the ground without placing stress on the Achilles tendon. Wear a tie shoe that is stiff soled and has a wide base, then add an over-the-counter or custom foot orthosis inside the shoe to prevent the twisting motion of the Achilles tendon due to over pronation. In the event that the tendon is unable to heal due to your life style or activity, you may have to be put in a walking cast for a short period to give it a chance to heal. You need to have the doctor, physical therapist, or come in to our facility to check for a leg length difference due to the walking cast being higher. This is to prevent any discomfort to the hips. After the tendon has healed and before the foot is taken out of the walking cast, range of motion at the ankle must be tested and if the foot is not allowed to properly bend upwards 15 degrees then the tightness in the calf will cause the foot to over pronate and reinjure. A stretching program will be needed to loosen up the calf muscle before much weight bearing is done without the cast. The stretching program can be found at the menu for feet hurt. If necessary a heel lift can be put in both shoes to help take the stress off the tendon. Should the tightness of the calves be the primary cause for the Achilles tendon damage and stretching has not loosen the Achilles tendon sufficiently, then discussion with your doctor for a calf release may have to be considered.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered the last resort and is often performed by an orthopedic surgeon. It is only recommended if all other treatment options have failed after at least six months. In this situation, badly damaged portions of the tendon may be removed. If the tendon has ruptured, surgery is necessary to re-attach the tendon. Rehabilitation, including stretching and strength exercises, is started soon after the surgery. In most cases, normal activities can be resumed after about 10 weeks. Return to competitive sport for some people may be delayed for about three to six months.
Prevention
If you're just getting started with your training, be sure to stretch after running, and start slowly, increasing your mileage by no more than 10% per week. Strengthen your calf muscles with exercises such as toe raises. Work low-impact cross-training activities, such as cycling and swimming, into your training.